Assay Development
Working with you, we will develop a robust and practical assay suitable for screening.
Optimization variables
Multiple assay conditions and assay types can be quickly surveyed using 384-well plates and our specialized equipment. Examples include cell density and treatment time for cell-based assays; concentration and incubation times to ensure linearity; and order of addition for biochemical assays.
Controls
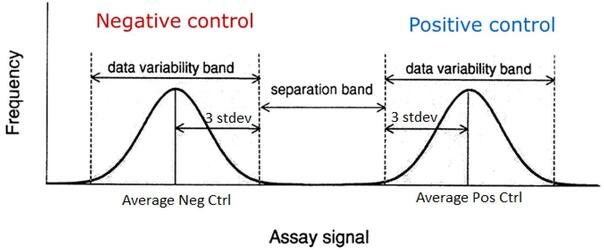
Assay-specific controls are used to ensure robust and reliable assay performance:
- negative control = vehicle (0% effect)
- positive control = mimics desired effect of screening hits (100% effect). Ideally, a positive control would be a drug for small molecule screening or an siRNA for siRNA screening.
Statistical measures of assay robustness
We use statistical measures of assay robustness, namely Signal to Background Ratio, Z’, and Coefficient of Variations for control populations, to drive assay development and assess screen readiness.
- Signal to Background Ratio (S/B) = Meanhigh signal control / Meanlow signal control
- Coeffiecient of Variation (CV) = (STDcontrol / Meancontrol )* 100
- Z’ = 1 - ((3STDpos control + 3STDneg control )/(Meanhigh signal control – Meanlow signal control))